Loops
In java, loops are sections of code that repeat while a certain condition is true. There is a common structure to all types of loops, such as:
- the control variable, called the loop counter
- this control variable must be initialized, i.e. it must have an initial value
- The increment/decrement of the control variable, which is modified each time the loop occurs
- The loop condition that determines if the looping should continue or the program should break from it.
While loops
This is how a standard while loop looks:
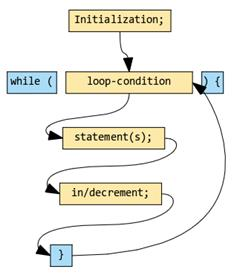
(source: https://www.developer.com/java/data/using-different-types-of-java-loops-looping-in-java.html\
Here's an example of a while loop in practice:
int counter = 1; // Control variable initialized
// Condition for loop continuation
while (counter <= 10) {
System.out.println(counter);
counter++; // Increment the control variable
}
/*
At the end of this loop, counter == 11, and the statements will have executed 10 times.
*/
Exercises
// 1.
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
while (a <= 15) {
b += 2;
a++;
}
// what is the value of 'b': ___ ?
// 2.
int a = 10;
int b = 1;
while (a < 0) {
b *= 2;
a--;
}
// what is the value of 'b': ___ ?
// 3.
int a = 2;
int b = 3;
int c = 4;
while (a < 10 || b < 15) {
c++;
a++;
b++;
}
// what is the value of 'a': ___ ?
For loops
For loops are very similar to while loops except they have different initialization techniques. This is how a standard for loop looks:
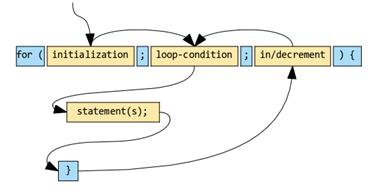
(source: https://www.developer.com/java/data/using-different-types-of-java-loops-looping-in-java.html\)
Here is an example of a for loop in practice:
// For(<initialization>;<condition>;<increment>
for(int counter = 1; counter <= 10; counter++){
System.out.println(counter);
}
// There are variations as well
int counter;
for( counter = 1; counter <= 10; counter++){
//... Statements
}
int counter = 1;
for(; counter <= 10; counter++){
//... Statements
}
int counter = 1;
for(; counter <= 10;){
//... Statements
counter++;
}
// Infinite loop
for(;true;);
Note: The condition check happens before the statements in the loop are executed. In addition, the increment statement happens after all the statements, a fact that many may overlook.
Exercises
// 1.
int a = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a += 10;
}
// what is the value of 'a': ___ ?
// 2.
int b = 0;
for (b = 1; b < 20; b++) {
b = b + b;
}
// what is the value of 'b': ___ ?
// 3.
int c = 7;
for (; c > 15; c++) {
c++;
}
// what is the value of 'c': ___ ?